IMO`s Second Generation Intact Stability Criteria
A second generation intact stability criteria is currently under development by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO). Unlike the first generation criteria this new criteria is physics based. The scope of the second generation intact stability criteria is to provide methods to assess ships which may be vulnerable to particular failure modes not adequately assessed by the existing criteria.
The four primary failure modes analysed are Parametric Roll, Broaching, Pure Loss of Stability & Dead Ship Stability.
Parametric Roll
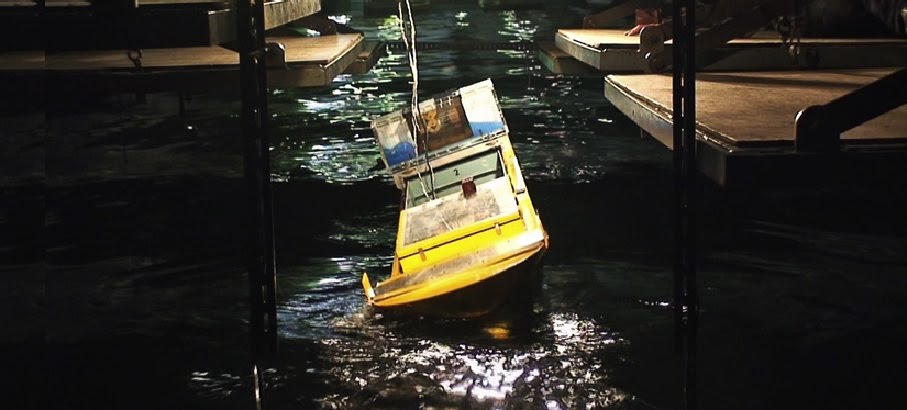
- In 1998, in the North Pacific, post-panamax container vessels rolled by 40 degrees. After that incident, many reports of similar rolling with other large container vessels and car carriers came up.
- One roll occurs with 2 waves
- The phenomenon couldn't be explained by linear theory.
- The cause is that the stability coefficient, which is a parameter in the rolling motion equation, changes periodically. (One of the parameter excitation phenomena)
Research topics
- Realization of presumable numerical simulation of parametric roll in random waves.
- Theoretical estimation of the probability of occurrence (local branch theory)

- Proposal and verification of IMO new standard draft (original draft in 2010 of the new vessel and anti-rolling tank to prevent parametric rolling (two patents are established)).
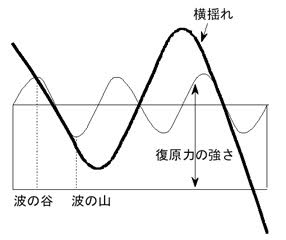
Numerical prediction of parametric rolling
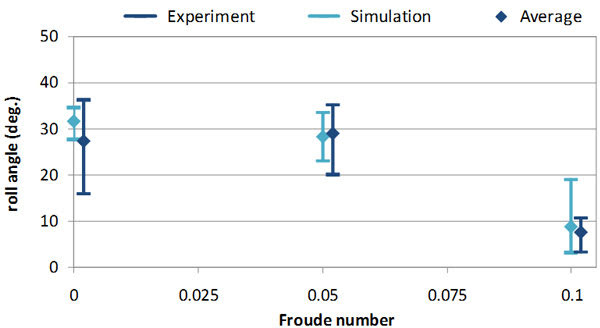
Maximum roll angle due to parametric roll of class C11 container ship during irregular heading
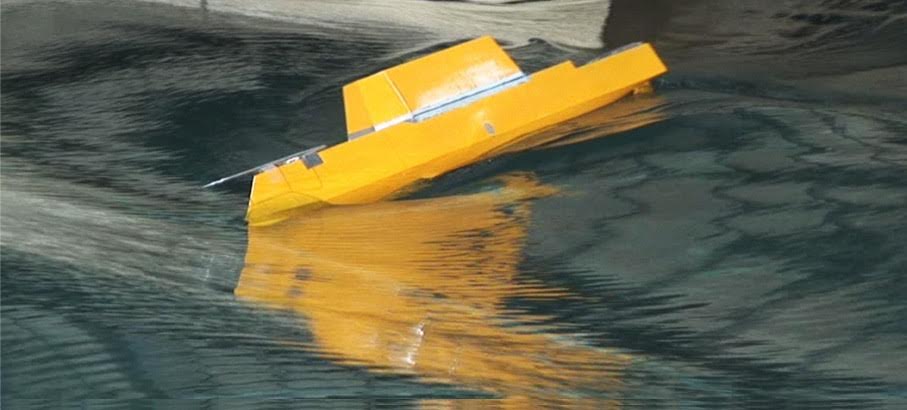
Broaching
- A wave riding phenomenon occurs in which the ship is captured in the downward wave front, and even if maximum steering effort is made, it is not possible to maintain course, and intense turning movement occurs. It is exposed to the danger of capsizing by the centrifugal force.
- Dynamically, it is a phenomenon in which periodic motion extracted by waves transitions to aperiodic motion, which can be explained by the global bifurcation theory of nonlinear dynamics.
- The phenomenon mostly occurs in car carriers, ships, yachts, etc. with a Froude number exceeding 0.3
Research topics
- Realization of numerical simulation that can estimate broaching in regular waves.
- Proposal of theory that can directly estimate the occurrence conditions of broaching and wave riding (global branch theory).
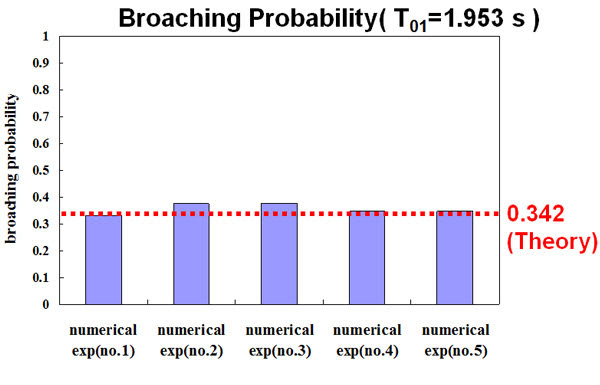
- Proposal and Verification of Broaching Probability Estimation Method in Random Waves
- Drafting standards to IMO (Japan-US joint proposal).
- Broaching prevention device.

Estimation of broaching occurrence probability
Pure Loss of Stability
- Large Car Carriers are prone to this failure mode.
- The transverse stability is significantly reduced when the crest of waves is at the centre of the ship.
- The horizontal tilt causes the under water shape to become asymmetrical, causing meandering motion, its centrifugal force increases the roll angle further.
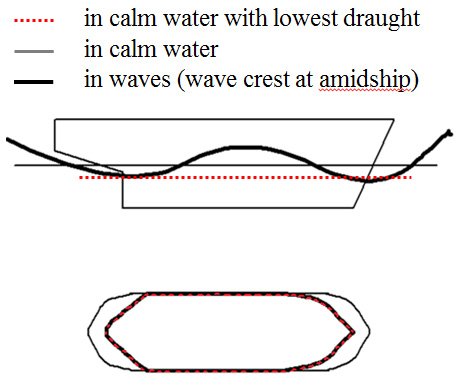
Prediction of the loss of stability during the aftermath
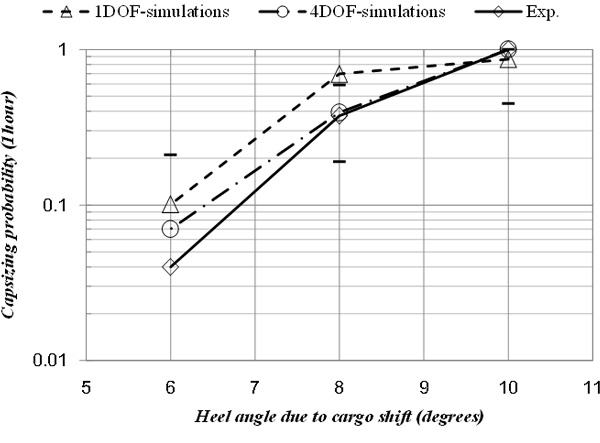
Dead Ship Stability
Research topics
- Capsizing model experiment in irregular beam wave and wind
- Improvement and experimental verification of the theory of estimation of capsizing probability in irregular beam wave and wind
- Verification and improvement of draft standards being submitted from Japan to IMO.