Application of Use of Geomagnetic Field in Migration of Aquatic Animals to Navigation of Underwater Vehicles
@
Abstract
A long-range cruising tye autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) mainly uses
an Inertia Navigation@System mounted on the vehilce and several underwater
acoustic trasnponders set up on the seafloor at the distance of about 30
km for its navigation. AUV can reach the final goal by improving the localization
eroors by INS at each underwater acoustic trasnponder. This system requires
a lot of the nderwater acoustic trasnponders for a long-range cruising
in the range of more than 1,000 km.
We paid attention to sea turtle migration using geomagnetic information studied by Lohmann, 1994. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2001/10/1012_TVanimalnavigation.html
We have constructed a virtual navigation system using the information of
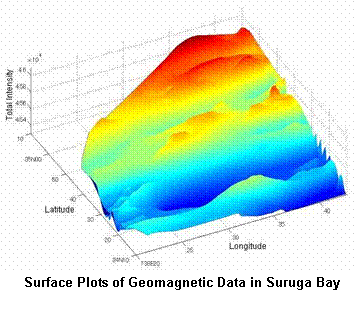
a geomagnetic sensor, a depth sensor and an altimeter. The system localizes
its position based on a geomagnetic field map and a bathmetric map.
We will carry out experiments using an underwater robot equippped with
a magnetic sensor a depth sensor and an altimeter in 2004.

Reference
P.@Katase,T. and Kato,N. "Application of Use of Geomagnetic Field in Migration of Aquatic
Animals to Navigation of Underwater Vehicles", 17th Symposium on Ocean
Engineering A2003
(in Japanese)
2. Shigetomi, T., Orimo,Y., Hamada,T and Kato,N. "Study on Underwater Navigation System For Long-Range Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Using Geomagnetic and Bathymetric Information", 3rd Int. Sym. on Aero Aqua Bio-mechanisms (ISABMEC2006), 2006
3. Hamada T., Shigetomi T. , Orimo Y. and Kato N., "Study on Underwater Navigation System For Long-range Autonomous Underwater Vehicles Using Geomagnetic and Bathymetric Information", Proc. of 14th Int. Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference,2007
@
@
@